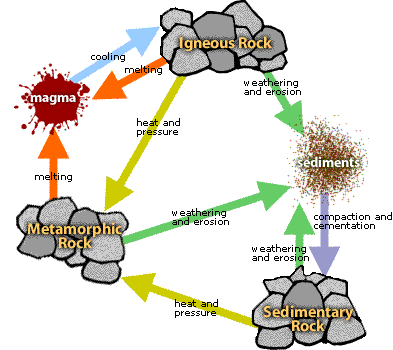
Metamorphic Rock: Rocks are formed by heat and pressure.
 Magma:
Magma: Melted rock inside the earth.
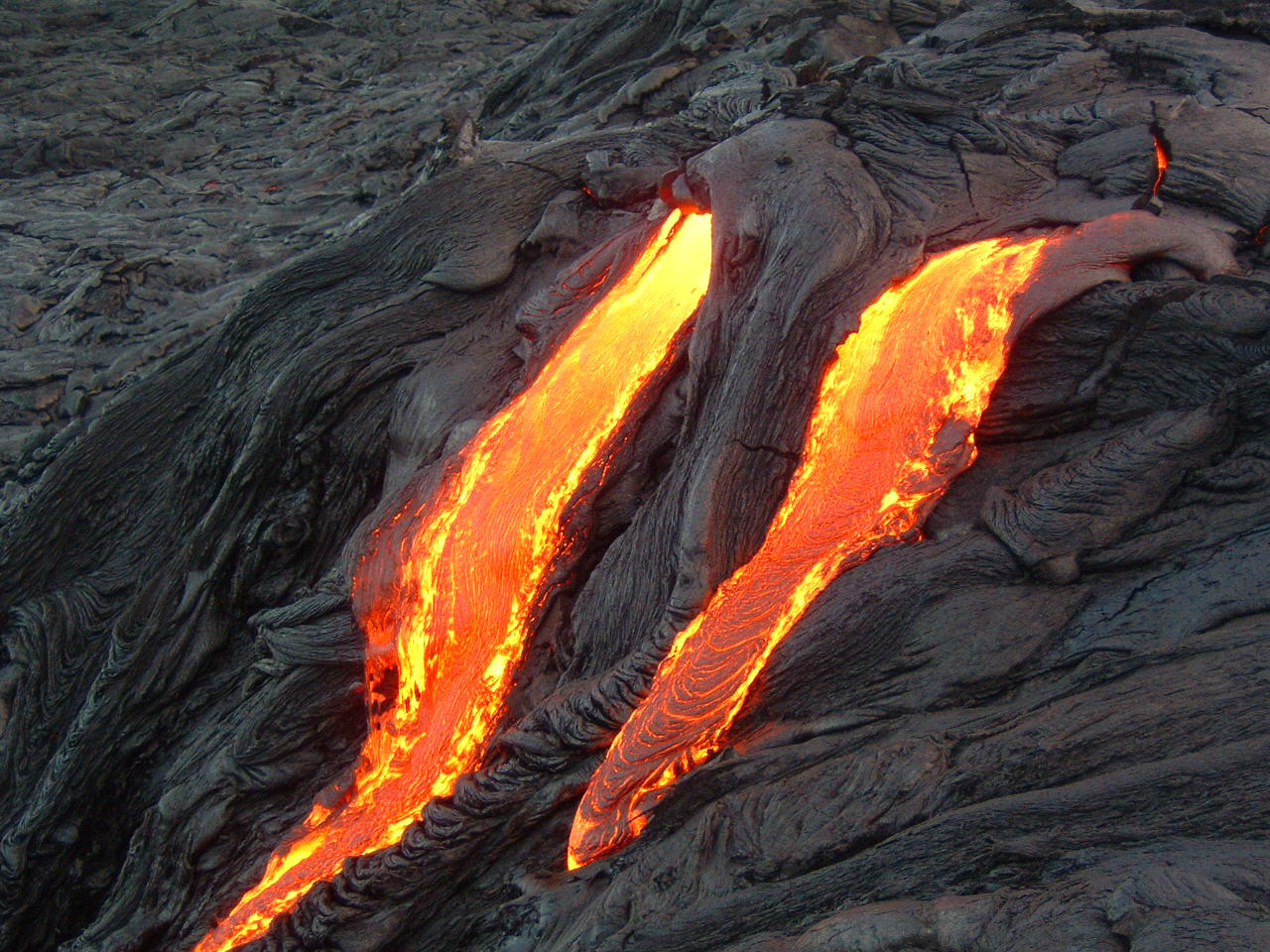
Lava: Molten rock outside the earth.
Solidification: It is a process in which lava cools down and become solid.
Igneous Rock: It is formed when lava cools down and become hard.
Weathering: Rock break down into pieces by wind, rain, and ice.
Erosion: When rocks are moved to other places.
Sediments: Small rocks broke into small pieces by weathering and erosion.
Compaction: When the sediments become together.
Cementation: When the sediments are glued together.
Sedimentary Rock: Its is formed by different types of sediments, when sediments gets glued together.